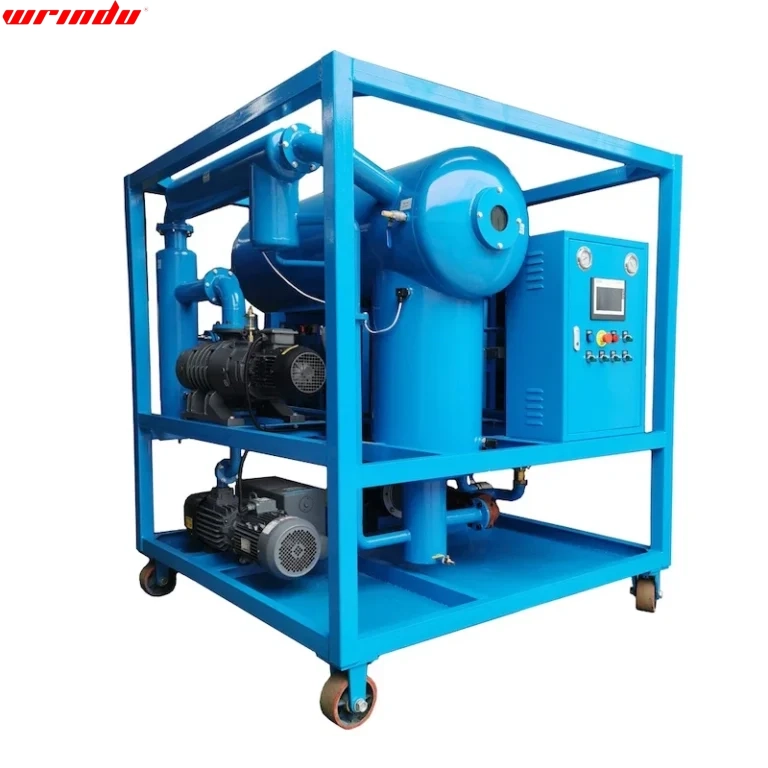
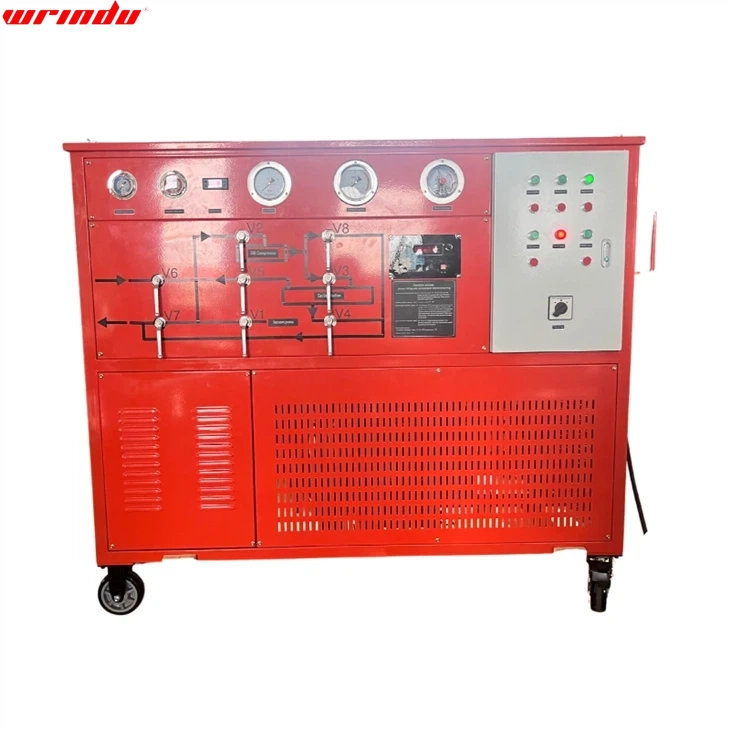
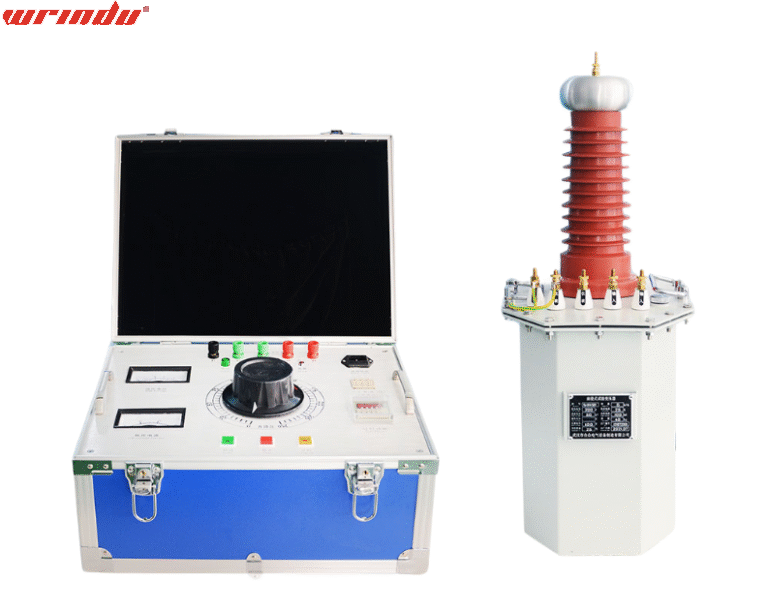
Hot Products
Year Experience
Production Lines
Cover Area
Experienced Staff
Total Solutions
Exported Countries
About Rui Du Mechanical and electrical (Shanghai) Co., Ltd
Rui Du Mechanical and electrical (Shanghai) Co., Ltd is an outstanding manufacturer of high-precision electrical power testing equipment, specializing in the research, development, manufacturing, and global marketing of transformer testing systems. With over a decade of rich experience in the field of high-end electrical testing equipment, customer satisfaction is our mission.
Professional Team
Our expert team delivers top-tier solutions with years of experience.

Legal Company
We operate fully legally, ensuring trust and compliance.
We support kinds of work sectors in the power industry.
Expert Technicians
Ruidu Co. employs a team of experts in high-voltage power testing and system solutions, skilled in designing, developing, and producing advanced equipment for applications.
Global Standards
Our products adhere to rigorous international certifications, including ISO 9001, IEC, and CE, which guarantee superior quality and reliability.
Good After-sale Service
Our after-sales team offers installation, training, and maintenance support. During the 12-month warranty, we provide free training, manuals, complaint response, and software upgrades. Lifelong maintenance and spare parts are available after warranty.
We Appreciate Feedbacks
Feedbacks
From Spain
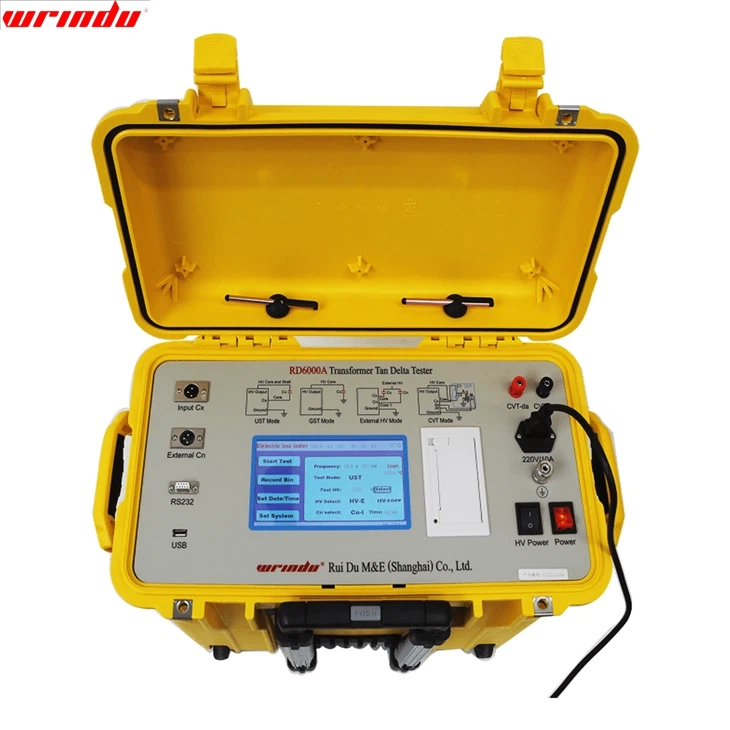
I am very satisfied with the RD6000A delta tan meter. Frequency conversion technology and clean power supply make measurements extremely accurate.
From Ukraine
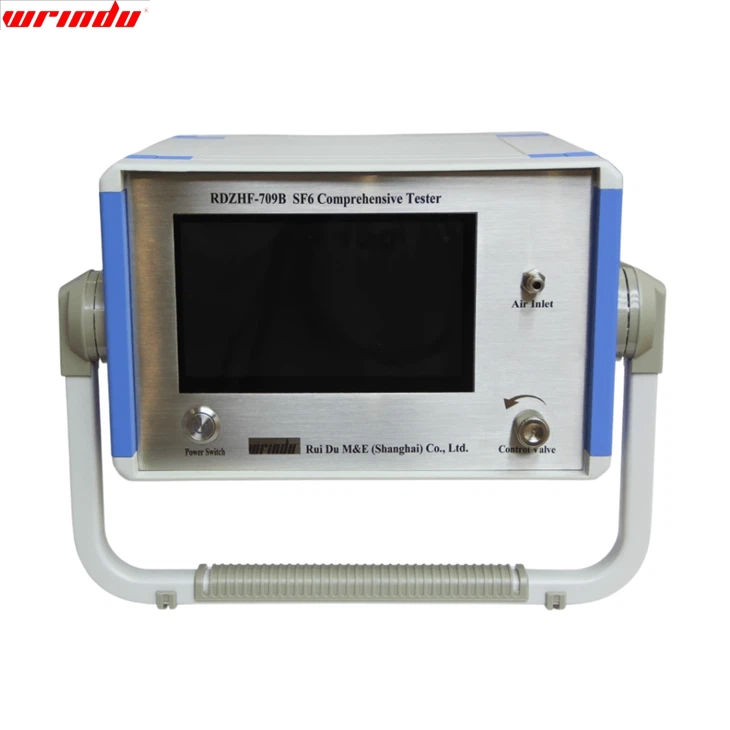
The RDZHF-709B SF6 comprehensive tester is so great! It’s efficient, combining humidity, purity, and decomposition product tests all in one device. And the results are really accurate.
From UK
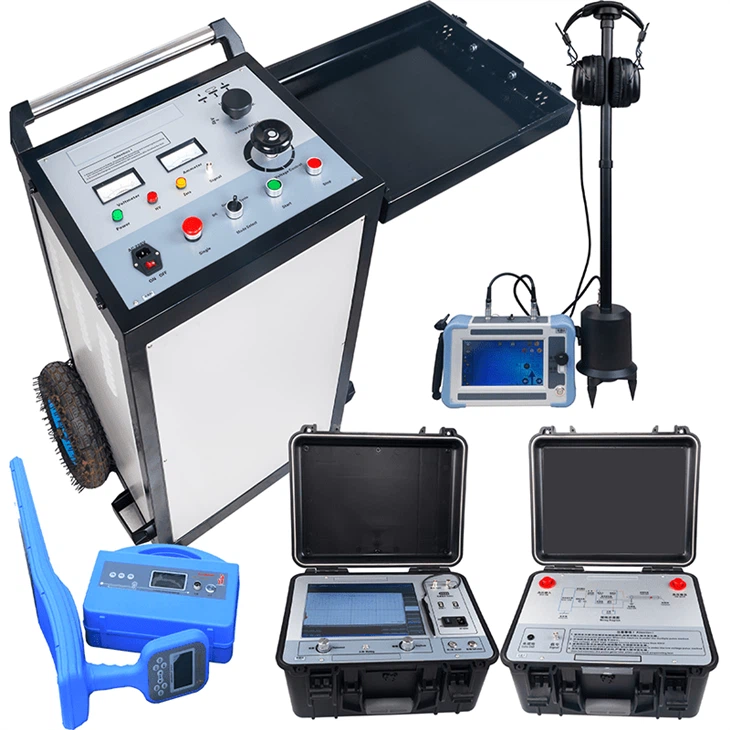
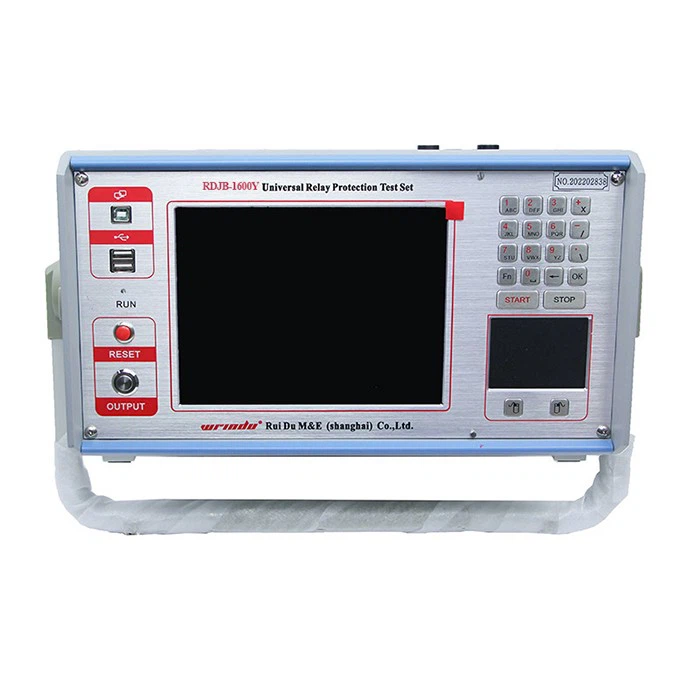
The Six-Phase Relay Protection Tester is an impressive and highly versatile device. Its ability to output six-phase voltage and current makes it ideal for a wide range of testing scenarios, from traditional setups to advanced three-phase transformer differential testing. It’s really Good!
From Kenya
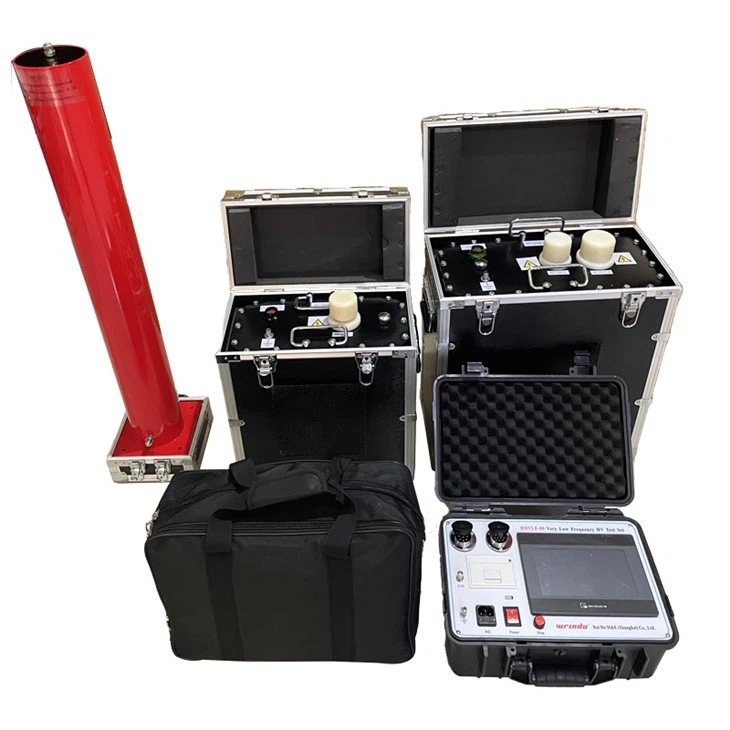
The functions of this ultra-low frequency dielectric loss tester are very powerful, equivalent to: ultra-low frequency withstand voltage test, insulation resistance test, dielectric loss test, partial discharge test, and DC high voltage leakage current test.
From Ethiopia
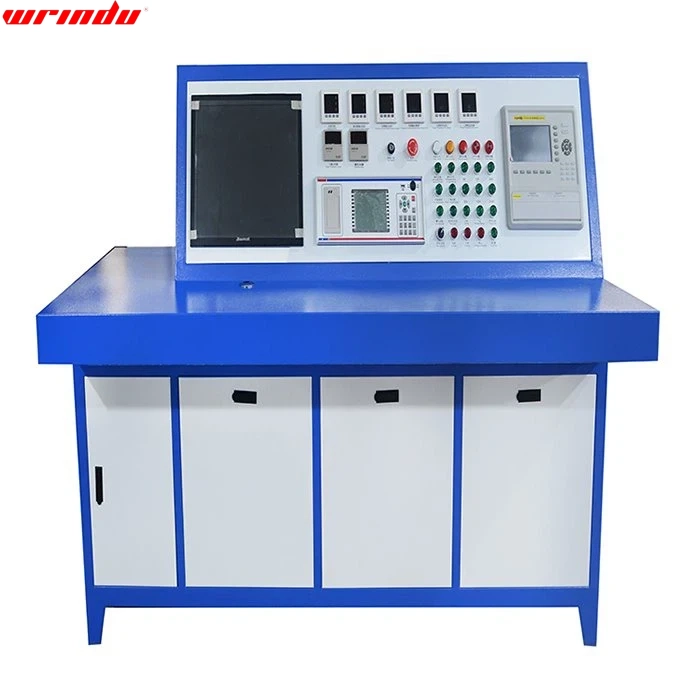
I am very satisfied with the RDTBT series transformer test bench. It is easy to operate, with a clear digital display, and the test results are really concise. It greatly improves testing efficiency and reliability.
From Vietnam
We have previously purchased our CT PT Analyzer and six-phase relay protection tester and are very satisfied with the quality and after-sales service of Redo. Recently, we are inquiring about the price of 15KV insulation resistance tester, dielectric response analyzer and 500KV series resonance device.