Power cable failures are caused by mechanical damage, environmental factors, electrical stress, and manufacturing defects. They are classified into series faults, parallel faults, and composite faults based on the type and location of the failure. Understanding these categories helps optimize fault detection with devices like faulty cable detectors.
How Are Power Cable Failures Caused?
Power cable failures result from multiple factors including mechanical damage (bending, crushing), environmental exposure (moisture, chemicals, UV radiation), electrical stresses (overload, surges), and aging or manufacturing defects. Improper installation and maintenance also accelerate failure rates, potentially leading to circuit faults or catastrophic outages.
Common causes include:
-
Mechanical stresses such as abrasion or conductor breakage.
-
Environmental wear from heat, moisture, or chemical infiltration.
-
Electrical overloading and transient voltage surges.
-
Aging insulation and protective sheath degradation.
What Are the Different Classifications of Power Cable Faults?
Cable faults are broadly classified as series faults, parallel faults, and composite faults based on their electrical characteristics:
-
Series faults: Disruptions or breaks in metallic conductors causing open circuits.
-
Parallel faults: Insulation failures causing short circuits or grounding.
-
Composite faults: Combination of conductor breaks and insulation failure.
This classification aids in selecting the appropriate fault detection and localization methods.
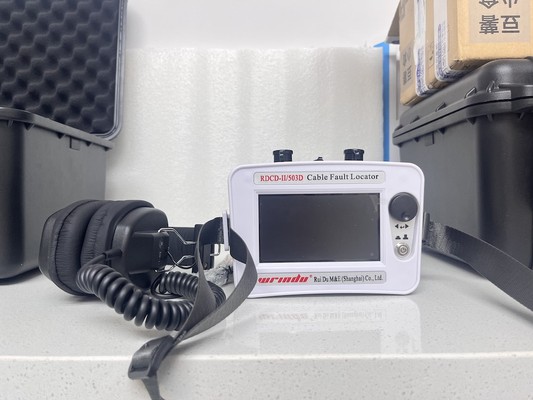

Which Fault Detection Methods Are Used for Power Cable Failures?
Various detection methods identify faults including time-domain reflectometry (TDR), impulse flashover, low voltage pulse, and electromagnetic sensing. Faulty cable detectors utilize these technologies to locate and classify faults precisely, aiding efficient repair.
Key techniques:
-
Pulse reflection to locate fault distance.
-
Impulse method for high resistance or flashover faults.
-
Acoustic or electromagnetic sensors for real-time fault detection.
-
Thermal imaging to identify hot spots.
Why Is Fault Classification Important for Cable Fault Detection?
Classifying faults into open circuit, low resistance, high resistance, or flashover categories streamlines diagnostic approaches. Each fault type demands specific detection methods for accuracy—for example, impulse flashover suits high resistance faults, while TDR excels at locating open circuits.
This targeted approach reduces downtime and repair costs by enhancing fault identification precision.
Who Are the Main Manufacturers and Suppliers of Faulty Cable Detectors?
China leads as a major manufacturing hub for power cable fault detection equipment. OEM factories and suppliers like Wrindu provide advanced, reliable faulty cable detectors featuring accuracy, customization, and competitive pricing for global wholesale markets.
Highlights include:
-
Certified products with ISO9001 and CE compliance.
-
Custom design capabilities tailored to client needs.
-
Factory-direct supply chain efficiencies for OEM and wholesale buyers.
When Should Power Cable Fault Testing Be Performed?
Fault testing should be conducted during regular maintenance, after electrical faults occur, and before commissioning new cable installations. Periodic inspections using faulty cable detectors prevent unexpected outages and ensure system reliability.
Recommended intervals:
-
Routine testing every 6-12 months in high-demand environments.
-
Immediate tests following surge events or insulation alarms.
-
Pre-commissioning tests after installation or repair.
Where Are Common Locations for Power Cable Failures?
Failures frequently occur at cable joints, terminations, bends, and where mechanical stresses concentrate. Underground sections are vulnerable to moisture and soil chemistry damage, while overhead cables face UV and temperature extremes.
Key vulnerability points:
-
Splice and termination points.
-
Areas of cable bending or compression.
-
Zones exposed to water ingress or rodent activity.
Does Using Advanced Faulty Cable Detectors Improve Cable Maintenance?
Yes, employing accurate faulty cable detectors improves maintenance by enabling quick fault location and classification. This reduces repair times, minimizes service interruptions, and extends cable lifespan, critical in industrial and utility power systems.
Advantages include:
-
Enhanced fault pinpointing reducing excavation and labor.
-
Early warning capability supporting preventive maintenance.
-
Integration with digital data systems for comprehensive asset management.
Are Composite Faults More Challenging to Detect?
Composite faults combine conductor breaks and insulation failure, making detection more complex. Specialized faulty cable detectors using multi-method technologies are required to accurately classify and locate such faults for effective remediation.
Detection complexity arises from:
-
Overlapping electrical signals from multiple fault types.
-
Variable fault resistance and insulation conditions.
-
Need for dynamic testing methods such as combined impulse and TDR.
Wrindu Expert Views
“Understanding and detecting power cable failures is central to maintaining grid reliability. At Wrindu, we develop state-of-the-art faulty cable detectors designed to meet the rigorous demands of industrial and utility environments worldwide. Our devices leverage advanced fault classification and precise localization technologies, enabling operators to prevent costly outages and improve maintenance efficiency. Coupled with customization options ideal for OEM and wholesale customers, Wrindu empowers energy professionals to excel in cable diagnostics.”
— Wrindu Cable Diagnostic Solutions Lead
Conclusion
Power cable failures stem from mechanical, environmental, electrical, and manufacturing origins, classified mainly as series, parallel, or composite faults. Faulty cable detectors play a critical role in identifying and locating these faults swiftly. Leading Chinese manufacturers like Wrindu offer reliable, customizable detection equipment suited for wholesale and OEM markets. Regular testing and proper fault classification enhance maintenance strategies, reduce downtime, and extend cable system life.
FAQs
Q1: What are the main causes of power cable failures?
Mechanical damage, environmental exposure, electrical stress, and aging insulation are primary causes.
Q2: How are power cable faults classified?
They are classified as series faults (open circuits), parallel faults (short circuits), and composite faults.
Q3: What detection methods are used for faulty cables?
Methods include TDR, impulse flashover, low voltage pulse, and acoustic/electromagnetic sensing.
Q4: Why is fault classification important?
It guides the selection of appropriate detection techniques, improving efficiency and accuracy.
Q5: How does Wrindu support cable fault detection needs?
Wrindu provides advanced, certified faulty cable detectors with OEM customization and global wholesale distribution.



