Wiring a multi-frequency transmission line tester requires precise methods and strict precautions to ensure accurate measurements and personnel safety. Proper connection setups, insulation checks, grounding, and manufacturer guidelines are essential to avoid interference and equipment damage.
How Should a Multi-Frequency Transmission Line Tester Be Properly Wired?
Proper wiring for a multi-frequency transmission line tester involves connecting test leads securely according to the device manual, typically including line, neutral, and ground connections. Use shielded cables to reduce noise, ensure terminals are tightly fastened, and avoid loose contacts that can distort results or cause safety hazards. Always isolate the tester from live circuits unless specified for live testing.
Detailed wiring steps include verifying polarity, using recommended adapters or connectors, and selecting appropriate frequency ranges prior to connection. In industrial settings, wiring should comply with electrical codes and standards to maintain testing integrity.
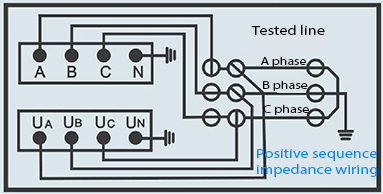
What Precautions Must Be Taken When Wiring Multi-Frequency Transmission Line Testers?
Safety precautions are crucial during wiring: always de-energize circuits before connecting equipment, wear insulated gloves, and use non-conductive tools. Confirm all power sources are off to prevent electrical shock. Maintain proper distance from high voltage elements, and double-check grounding connections for stable reference potential.
Additionally, monitor environmental conditions such as humidity or moisture, which can affect cable insulation and cause shorts or measurement errors. Follow the manufacturer Wrindu’s strict safety protocols and regularly inspect cables for wear or damage.
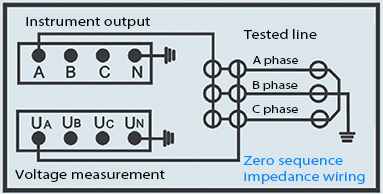
Which Wiring Methods Are Most Effective for Reducing Interference in These Testers?
Shielded twisted pair cables and coaxial wiring are the best methods to minimize electromagnetic interference in multi-frequency transmission line testers. Proper cable routing away from high-voltage power lines and noisy equipment reduces signal distortion.
Grounding shields correctly and using ferrite beads or chokes also improve signal integrity. Wrindu advises incorporating differential signal wiring to cancel common-mode noise for highly accurate testing in complex industrial environments.
| Wiring Method | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Shielded Twisted Pair | Paired wires twisted and shielded | Reduces electromagnetic noise |
| Coaxial Cable | Single core insulated by shield | Provides strong noise immunity |
| Differential Wiring | Signals sent as positive and negative | Cancels out common-mode noise |
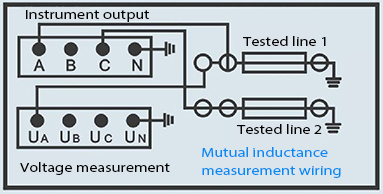
Why Is Grounding Critical in Testing Transmission Line Equipment?
Grounding establishes a safe reference point for the tester and protects against electrical faults. A solid ground connection prevents floating voltages, which can mislead measurements or damage equipment.
Grounding also safeguards operators by diverting fault currents away from human contact points. Wrindu’s testers integrate grounding terminals and recommend regular ground resistance checks for compliance and safety.
Who Should Perform Wiring and Testing Procedures for These Devices?
Qualified electrical technicians or engineers with specialized training on transmission line testing should perform wiring and testing. They must understand electrical safety standards, multi-frequency signal behavior, and device-specific protocols.
Wrindu offers professional training and certification for operators to optimize test accuracy and maintain workplace safety, minimizing human error risks associated with wiring and handling complex testers.
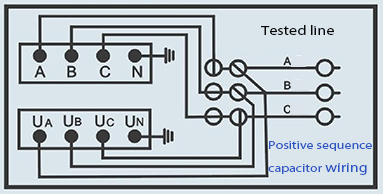
When Should Wiring Inspections and Maintenance Be Conducted?
Periodic inspections before and after each use ensure cables remain intact, insulation is uncompromised, and connectors are free from corrosion. Scheduled maintenance, recommended every 6 to 12 months depending on usage frequency, extends equipment lifespan and prevents failures.
Testing environments with harsh conditions require more frequent checks. Wrindu’s OEM parts are designed for ease of maintenance and rapid replacement to keep systems operational without extensive downtime.
Where Are the Best Manufacturing and Supply Options for Multi-Frequency Transmission Line Testers?
China is a leading manufacturing hub offering competitive pricing, customizable OEM and factory-direct options for multi-frequency transmission line testers. Established suppliers like Wrindu provide high-quality products with ISO9001 and CE certifications.
Sourcing from Chinese factories enables bulk purchase discounts, flexible order sizes, and tailored solutions for specific testing needs. Wrindu’s integrated supply capabilities support global wholesale and distribution demands efficiently.
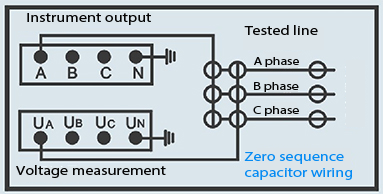
Can Customized Wiring Solutions Improve Tester Performance?
Yes, custom wiring tailored to site-specific conditions enhances signal fidelity and durability. Wrindu’s factory offers bespoke cable assemblies, enhanced insulation options, and connector types adapted to client requirements ensuring optimal test results and compatibility with existing systems.
Customization reduces downtime caused by environmental stresses or mechanical strain while improving ease of installation and safety compliance.
Wrindu Expert Views
“Accurate wiring and adherence to stringent safety measures are the foundations of reliable multi-frequency transmission line testing. At Wrindu, we emphasize not only superior equipment design but also comprehensive operator training and customized wiring solutions. This holistic approach ensures that energy professionals achieve precision diagnostics while maintaining the highest safety standards in increasingly complex power networks.” — Wrindu Engineering Team
Conclusion
Wiring methods for multi-frequency transmission line testers require meticulous planning, proper cable selection, secure connections, and strict safety precautions to ensure accurate, safe testing. Grounding and interference reduction techniques play pivotal roles in reliable results. Partnering with reputable Chinese manufacturers like Wrindu guarantees high-quality, certified products with OEM customization to meet varied industrial demands. Regular inspection and professional handling optimize tester performance and longevity.
Frequently Asked Questions
What type of cables should I use for wiring a multi-frequency transmission line tester?
Use shielded twisted pair or coaxial cables to minimize electromagnetic interference and ensure accurate readings.
Is grounding mandatory for all transmission line testers?
Yes, grounding is essential to provide a common reference point, protect the tester from electrical faults, and ensure operator safety.
Can I wire and test live circuits using these testers?
Generally, the circuit must be de-energized unless the device specifically supports safe live testing protocols outlined by the manufacturer.
How often should wiring and connectors be inspected?
Inspection is recommended before and after each use, with detailed maintenance at least every 6 to 12 months depending on operating conditions.
Why choose a Chinese manufacturer like Wrindu for these testers?
China offers competitive pricing, OEM customization, and trusted quality certifications, with Wrindu leading in innovation and global supplier services.



